Knowledge base
1000 FAQs, 500 tutorials and explanatory videos. Here, there are only solutions!
Understanding the difference between Domain and DNS Zone
This guide explains how a domain name and a DNS zone work.
Preamble
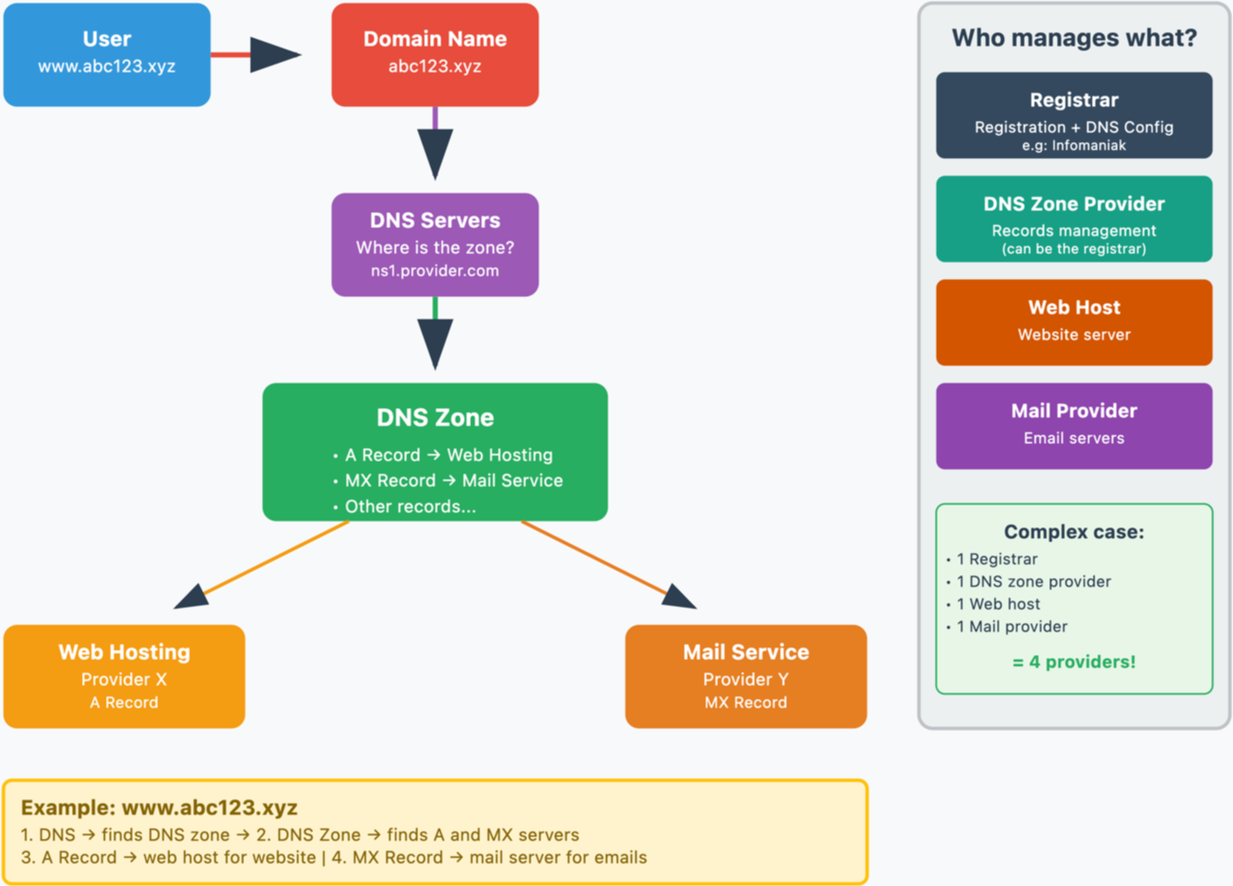
- When you browse a website
https://www.abc123.xyzfor example,abc123.xyzis the domain name. - Each domain name has DNS (Domain Name System), which indicate where (with which provider, for example) the DNS zone is located.
- The DNS zone then allows the management of various services related to the domain name to be entrusted to different providers.
- For a unique domain name, it is possible, for example, to entrust:
- web hosting to provider X (via the "
A" type record) - and the Mail Service to provider Y (via the "
MX" type record)
- web hosting to provider X (via the "
- For a unique domain name, it is possible, for example, to entrust:
Domain name, DNS and DNS zone, then services
Who manages what?
- Each domain name is reserved and managed by a registrar (registration office). For example, Infomaniak is a registrar, one of the cheapest in Switzerland.
- The DNS of a domain name are configured with the registrar managing the domain name.
- The DNS zone can be handled by the registrar or another provider.
- Web hosting and the Mail Service can be handled by any host.
In the most complex case, it is therefore possible to have 1 different provider for the following services: domain name reservation and DNS management, DNS zone management, web hosting, Mail Service.
The following diagram summarizes these different possibilities with the involvement of different providers:
Infomaniak
As a registrar and host, Infomaniak can manage all these services. It's the simplest solution.
- In the case of Infomaniak, the DNS are generally of the form nsXX.infomaniak.com and nsXX.infomaniak.com (XX like 11 or 12 for example).
- You can modify the DNS of your domain name, as well as modify the "inside" of these DNS i.e. modify the DNS zone of a domain name.
And in these DNS zones, to redirect traffic to services, we distinguish:
- an MX record that allows you to point a domain name (
domain.xyzfor example) to a mail server. - an A record that allows you to point a domain name (
domain.xyzfor example) or a subdomain (example.domain.xyzfor example) to a web server that has a static IP address (otherwise you would have to constantly edit the A record to provide the new IP address - see this other guide on this subject)
Some possible situations
Examples and fictitious names
| All services are with Infomaniak | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| domain name | domain.xyz | registered with -> | Infomaniak |
| DNS of the domain name | ns1.infomaniak.com… | so DNS zone must exist at -> | Infomaniak |
| site hosted by -> | Infomaniak | so DNS zone must contain A record | 123.45.67.8 for example |
| mail hosted by -> | Infomaniak | so DNS zone must contain MX record | mx-mail.maniak for example |
| All services are with Infomaniak except mail | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| domain name | domain.xyz | registered with -> | Infomaniak |
| Domain name DNS | ns1.infomaniak.com… | so the DNS zone must exist at -> | Infomaniak |
| website hosted by -> | Infomaniak | so the DNS zone must contain A record | 123.45.67.8 for example |
| mail hosted by -> | Medical Service | so the DNS zone must contain MX record | med-mx.net for example |
| All services are with Infomaniak except the website | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| domain name | domain.xyz | registered with -> | Infomaniak |
| Domain DNS | ns1.infomaniak.com… | so DNS zone must exist with -> | Infomaniak |
| site hosted by -> | Clinic | so DNS zone must contain A record | 9.87.65.4 for example |
| mail hosted by -> | Infomaniak | so DNS zone must contain MX record | mx-mail.maniak for example |
| All services are with Infomaniak except the domain name | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| domain name | domain.xyz | registered with -> | GoMamie |
| DNS of the domain name | ns1.infomaniak.com… | so the DNS zone must exist with -> | Infomaniak |
| site hosted by -> | Infomaniak | so the DNS zone must contain A record | 123.45.67.8 for example |
| mail hosted by -> | Infomaniak | thus the DNS zone must contain MX records | mx-mail.maniak for example |
| All services are with Infomaniak except the DNS zone | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| domain name | domain.xyz | registered with -> | Infomaniak |
| DNS of the domain name | ns.privateDNS.org... | thus the DNS zone must exist with -> | Private DNS |
| site hosted by -> | Infomaniak | so DNS zone must contain A record | 123.45.67.8 for example |
| mail hosted by -> | Infomaniak | so DNS zone must contain MX record | mx-mail.maniak for example |
| No service exists with Infomaniak except the domain name | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| domain name | domain.xyz | registered with -> | Infomaniak |
| DNS of the domain name | ns.privateDNS.org… | so DNS zone must exist with -> | Private DNS |
| hosted by -> | Clinic | so the DNS zone must contain A record | 9.87.65.4 for example |
| hosted by -> | Medical Service | so the DNS zone must contain MX record | med-mx.net for example |
| No service exists with Infomaniak except the DNS zone | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| domain name | domain.xyz | registered with -> | GoMamie |
| Domain name DNS | ns1.infomaniak.com… | so the DNS zone must exist at -> | Infomaniak |
| site hosted by -> | Clinic | so the DNS zone must contain A record | 9.87.65.4 for example |
| mail hosted by -> | Medical Service | so the DNS zone must contain MX record | med-mx.net for example |
| No service exists with Infomaniak except mail | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| domain name | domain.xyz | registered with -> | GoMamie |
| domain name DNS | ns.privateDNS.org... | so DNS zone must exist with -> | Private DNS |
| site hosted by -> | Clinic | so DNS zone must contain A record | 9.87.65.4 for example |
| mail hosted by -> | Infomaniak | so DNS zone must contain MX record | mx-mail.maniak for example |
etc.
Link to this FAQ:

