Knowledge base
1000 FAQs, 500 tutorials and instructional videos. Here, there are only solutions!
Modify the web site's server configuration
This guide explains how to modify the server configuration of a site on Web Hosting Infomaniak.
Preamble
- Apache is the HTTP server.
- It is configured with a
.htaccessfile placed at the root of the website.
- It is configured with a
- PHP is a programming language used to create dynamic web pages via an HTTP server.
- It is possible to customize the PHP directives with a
.user.inifile, which will be effective in the folders and subfolders of the location of the .user.ini file.
- It is possible to customize the PHP directives with a
- Refer to this other guide regarding the creation of .htaccess & .user.ini files.
Modify the server configuration of a site…
… via the Manager
To modify the PHP configuration and most of the parameters (max_input_vars, allow_url_fopen, memory_limit, post_max_size + upload_max_filesize, etc.):
- Click here to access the management of your product on the Infomaniak Manager (need help?).
- Click directly on the name assigned to the product concerned.
- Click on Manage under Advanced Settings:
- Click on the different tabs General, PHP / Apache and PHP Extensions to proceed with the desired adjustments:
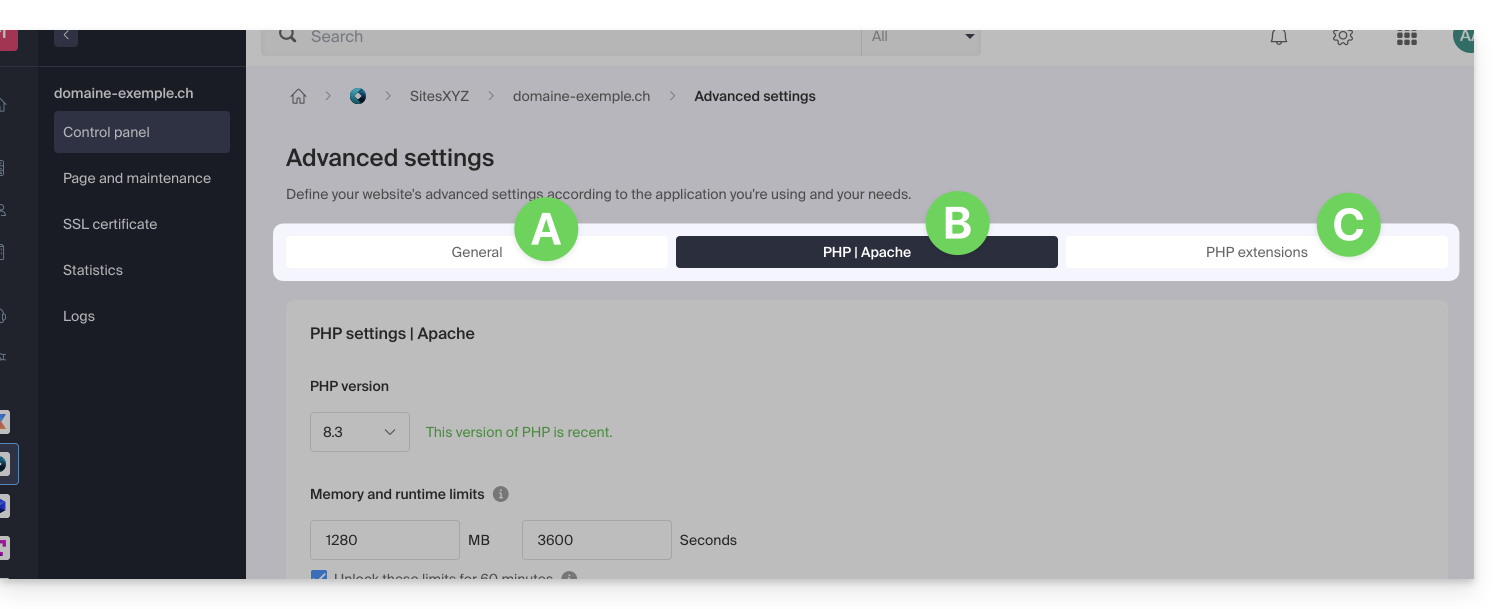
Do not forget to save the changes at the bottom of the page.
Refer to this other guide if you are looking for information regarding limit values and the possibilities of unlocking the latter.
… via the .user.ini file
For PHP directives that are not present on the Manager side, it is necessary to define the desired values in the .user.ini file, for example:
max_file_uploads = 20The list of existing directives can be found on the official PHP website but the elements with the indication PHP_INI_SYSTEM in the Modifiable column as well as max_input_time, memory_limit and mysqli.default_socket are not usable.
… in CLI
To customize PHP directives when executing scripts in command line (CLI) or in CRON tasks, it is necessary to specify the desired values in a .user.ini file.
Then, to apply these configurations, the PHP executable is used with the -c option followed by the path to the .user.ini file.
For example, to modify the memory limit available for PHP to 1024M, you can create or modify the .user.ini file using the following command:
echo 'memory_limit = 1024M' > .user.iniThis command writes the memory_limit directive with the value 1024M in the .user.ini file.
Next, when executing a PHP script from the command line or in a CRON task, use the PHP command with the -c option to specify the .user.ini file containing the custom configurations.
The following example enables allow_url_fopen for the WP CLI tool (allows, among other things, retrieving extensions):
php -d allow_url_fopen=On ~/bin/wp package install trepmal/wp-revisions-cliphp: the PHP executable-d allow_url_fopen=On: the-doption allows setting a PHP configuration directive (allow_url_fopen) with the valueOn~/bin/wp: path to the WP CLI executablepackage install trepmal/wp-revisions-cli: the specific command to install the WP CLI packagetrepmal/wp-revisions-cli
This ensures that the allow_url_fopen option is enabled during the execution of the specified WP CLI command. Enabling allow_url_fopen may be necessary for certain operations that involve opening remote URLs, such as downloading extensions or packages. Make sure this option is enabled securely and in accordance with best security practices.
Link to this FAQ:
Has this FAQ been helpful?